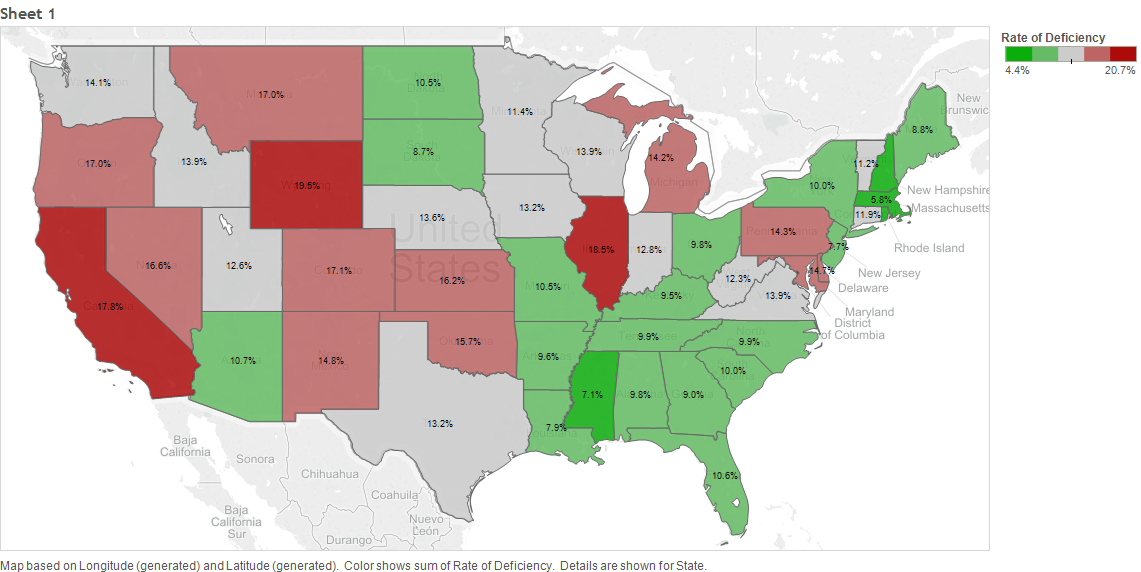
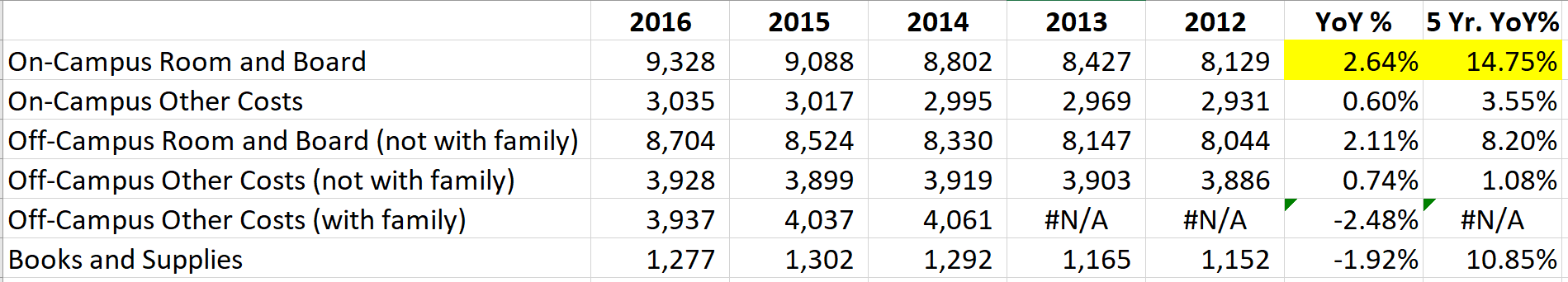
The Carnegie Classification™ has been the major institutional framework for describing higher education institutions since 1970. This classification system comes out approximately every five years with the latest rendition released on February 1, 2016. This release represents the initial data provided by the Indiana University Bloomington Center for Postsecondary Research that took over the responsibility from the Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching. The Carnegie name and brand were retained.
The Carnegie Classification has six parallel classifications as follows: Basic (the traditional Carnegie Classification framework), Undergraduate and Graduate Instructional Program, Enrollment Profile and Undergraduate Profile, and Size & Setting. These classifications provide different lenses through which to view U.S. colleges and universities, offering researchers greater analytic flexibility. A total of 4,663 institutions are categorized under this system in the 2015 release.

There were a number of changes to the classifications in 2015. Most notable is the introduction of new Associates Colleges categories, which are broken down based on program and student mix. Additional two-year institutions referred to as “special-focus” are placed in separate categories, parallel to how four-year special-focus institutions are designated. These institutions typically have concentrations in specific specialty areas such as health fields.
In addition to the classifications, a number of additional metrics are provided. For example, ACT and SAT statistics are provided which were used in the construction of the classifications. By clicking HERE, you can download a spreadsheet that provides a detailed list of 4,663 U.S. institutions across the six seperate Carnegie Classifications. You can also browse through the various 2015 classifications and additional data in Public Insight.